Cannabinoids in the brain: their mechanism of action in relation to neuropsychiatric disorders
Authors:
Valentina Cinquina1, PhD
DDr. Ana Weidenauer2
Univ.-Prof. Dr. h. c. Dr. Siegfried Kasper1
Univ.-Prof. Dr. Tibor Harkany1,3
1Department of Molecular Neurosciences
Center for Brain Research
Medical University of Vienna
2Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy
Medical University of Vienna
3Department of Neuroscience
Karolinska Institutet
Sweden
Corresponding author:
Univ.-Prof. Dr. Tibor Harkany
E-Mail: Tibor.Harkany@meduniwien.ac.at
Sie sind bereits registriert?
Loggen Sie sich mit Ihrem Universimed-Benutzerkonto ein:
Sie sind noch nicht registriert?
Registrieren Sie sich jetzt kostenlos auf universimed.com und erhalten Sie Zugang zu allen Artikeln, bewerten Sie Inhalte und speichern Sie interessante Beiträge in Ihrem persönlichen Bereich
zum späteren Lesen. Ihre Registrierung ist für alle Unversimed-Portale gültig. (inkl. allgemeineplus.at & med-Diplom.at)
Understanding how the endogenous cannabinoid system operates laid foundations to rationalizing the action of the major plant-derived cannabinoids, ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol. Here, the progressive emergence of plant-derived cannabinoids in medical practice is illustrated by their potential relevance to the treatment of schizophrenia and epilepsy.
Keypoints
-
Cannabis sativa contains >100 bioactive cannabinoids, therpens and flavonoids, not only Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol.
-
The endocannabinoid system is the molecular target for THC to affect neuronal structure and function.
-
THC effects on synaptic neurotransmission are short-lived and reversible in adults. In contrast, THC exposure in utero or during adolescence can disrupt the brain’s connectome and adversely affect cellular energy utilization for life.
Introduction: a tale of recreational use and therapy
Evolutionary biology posits the existence of Cannabis sativa for the last 600 million years. Co-evolution with humans was because of the plant’s richness in durable fiber rather than its perceived psychotropic significance. The first mention of Cannabis sativa in relation to a discrete medical condition, pain, was in ancient China ~4000 B.C., and included detailed knowledge on the plant’s psychotropism, which suggests a significant content in ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). During the ensuing millennia, medical benefits of Cannabis spp. were repeatedly mentioned by Greeks, Romans, Mongols and others. Written records show the widespread use of cannabis extracts for medicinal purposes by the 19th century. In 1937, however, its assumed abuse potential led to the banning of marijuana from further medicinal use in the United States. The beginning of a substantial and progressive shift of research, medical and legislative positions on plant-derived cannabinoids can probably be pinned to 1967, when THC was isolated and chemically characterized1,2, and recognized as the main psychoactive constituent of Cannabis sativa.
Subsequent chemical analyses showed that THC is just one of the many bioactive compounds in the host plant: by now >100 cannabinoid-family compounds (collectively referred to as “phytocannabinoids”), as well as many other substances (therpens, flavonoids) that might also produce marked bodily responses in humans are distinguished. By broad definition, phytocannabinoids are separated into groups of “drug-type” and “fiber-type” substances. The former group includes THC and its derivatives (tetrahydrocannabivarin, THC-acid) with psychoactive effects. The latter group, in turn, is a conglomerate of non-psychoactive cannabinoids like cannabidiol (CBD), cannabigerol and cannabidivarin. The rapid expansion of knowledge on phytocannabinoids together with the increasing social acceptance of cannabis as a moderately addictive drug in adult users generated significant interest in both phytocannabinoid-based and synthetic cannabinoid therapies (for, e.g., pain, osteoporosis, neuropathies, neurodegeneration, epilepsy, inflammation and cancer).
Enrichment in cannabinoids by selective cultivation
Originally, herbal cannabis contained minute amounts of psychoactive constituents, which accumulated in floral oils likely to repel insects. To meet the demand of increasing cannabis consumption for its psychoactive potency worldwide, significant advances in selective cultivation and hybrid production ensued. This, together with improved extraction and preparative procedures, helped to maximize the THC (but also CBD) content. Worryingly, herbal mixtures that contain powerful synthetic additives (such as “Spice”) are increasingly abused alike new generations of synthetic cannabinoids that are ~10-200x more potent than THC and typically do not contain CBD.3,4
Cannabinoid receptors as molecular targets for THC and related ligands
The effects of THC (and many others cannabinoids but CBD) are chiefly mediated by two members of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family: cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1R) and its orthologue, CB2R. Both receptors recruit Gi/G0 proteins, whose Gαi subunit inhibits adenylate cyclase. CB1Rs also modulate ion channels, inducing the inhibition of voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels and activation of G protein-activated inwardly-rectifying K+ channels.5,6 This mechanism is of primary importance in excitable tissues and leads to the inhibition of exocytosis upon cell depolarization (that is, negative regulation of neurotransmitter release and hormone secretion in the nervous system and at the periphery, respectively). CB1R/CB2R, via Gβγ, also modulate pleiotropic intracellular signaling cascades, including mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (Jun), p38 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt. These systems are fundamental to the regulation of cell proliferation, cell cycle control and cell death. Moreover, CB1Rs regulate cellular metabolic processes through the intracellular release of ceramide by interaction with neutral sphingomyelinase via FAN.7 Besides CB1R and CB2R, endocannabinoid (and phytocannabinoid) action is transduced by a variety of alternative receptors, including TRPV1, GPR55 and PPARs. In contrast to THC, CBD action is considered largely non-CB1R-mediated. Even if alternative cannabinoid receptors (TRPV1, GPR55, PPARs) might play a role, the enhancement of antioxidant defense and direct action on mitochondrial bioenergetics are favored.
CB1Rs are the most abundant GPCRs in the mammalian brain, primarily expressed in neurons and to a lesser extent in astroglia.8 CB1Rs concentrate in areas controlling motor, cognitive, emotional and sensory functions (e.g., the hippocampus, basal ganglia, cerebellum, cerebral cortex and olfactory bulb).9,10 Foci of CB1Rs are also found in areas controlling pain (brainstem), body temperature, sleep-wake cycles (hypothalamus), and hormone secretion (pituitary).11 Beyond the nervous system, CB1R expression was reported in the eye, muscle, pancreas, heart, lung,12-15 placenta and myometrium,16-18 highlighting its role in body-wide homeostatic control.
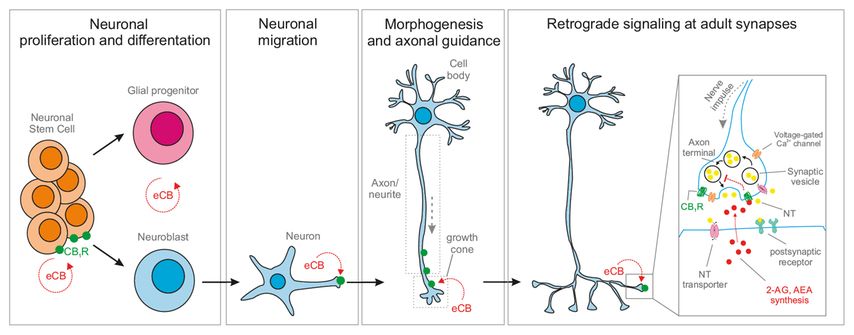
Fig. 1: Endocannabinoid action through CB1R during neuronal differentiation, and the endocannabinoid-mediated control of synaptic neurotransmission in adult brain. Abbreviations: CB1R, CB1 cannabinoid receptor; eCB, endocannabinoid; NT, neurotransmitter
CB2Rs are classically associated with cells of the immune lineage. Within the brain, CB2Rs were unequivocally detected in perivascular microglia and vascular endothelial cells. CB2Rs in neurons (particularly in the brainstem) remain a contentious issue.19 Increased CB2R expression, possibly owing to infiltration of immune cells and activation of microglia, is recognized in certain neurodegenerative disorders.20
Mechanism of action: THC impairs endocannabinoid signaling
The discovery of cannabinoid receptors led to the rapid identification of a family of small unsaturated fatty acids (eicosanoids) as their natural ligands.21-23 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) and anandamide (AEA) are the best-characterized endocannabinoids. Endocannabinoids are produced primary “on demand” from membrane lipid precursors by multiple biosynthetic pathways24 and reach their receptors by (facilitated) diffusion. AEA is formed by the cleavage of its phospholipid precursor, N-arachidonoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine (NArPE).25,26 By contrast, sn-1-diacylglycerol lipase (DAGL) α/β are responsible for the synthesis of 2-AG.27 Endocannabinoid signaling is terminated by enzymatic hydrolysis: fatty acid amide hydrolases (FAAH1/2) inactivate AEA,28,29 while monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) and ABHD6 catabolize 2-AG.30-32 Moreover, AEA can be oxygenated by cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), 5-,12- and 15-lipoxygenase (5-/12-/15-LOX), and by several cytochrome P450 monooxygenases.29
In the adult brain and spinal cord, the signaling paradigm for endocannabinoids is their activity-dependent (Ca2+-dependent) short-lived production in postsynaptic neurons. This is followed by endocannabinoid diffusion (in a 20-100 µm radius) towards presynaptic terminals endowed with CB1Rs, followed by signal transduction. Upon endocannabinoid binding, CB1Rs internalize and endocannabinoids become rapidly inactivated by hydrolysis.33 Endocannabinoid signaling in the developing nervous system is also CB1R dependent, and primarily associated with stem cell renewal, cell migration and axonal pathfinding.34 In both cases, THC can produce unwanted CB1R occupancy for periods longer than produced by physiological endocannabinoid signals, thus changing the timing of both synaptic neurotransmission and neurocircuit maturation in adult and developing brain, respectively.
Long-lived THC effects during pre- and postnatal brain development
Endocannabinoids control at least 6 stages of cellular development in the brain: i) stem cell division, ii) primary fate decisions of neuronal progenitors, iii) survival of progeny, iv) neuronal migration, v) neuronal morphogenesis with particular impact on neurite outgrowth and vi) synaptogenesis.35-37 To orchestrate stages iv-vi, CB1Rs are localized on the surface of distal axons segments35,38 including growth cones to modulate directional steering decisions.39,40 The presence of CB1Rs on elongating neurites explains why THC is particularly detrimental for ordered brain connectivity to evolve. Given that THC efficiently crosses the placenta,41,42 is detectable for hours to several days and lipophilic, maternal THC intake can be powerful to disrupt the temporal precision of physiological endocannabinoid action. Even more so, THC is not inactivated by any of the known endocannabinoid hydrolases. Thus, THC can engage CB1Rs prematurely and even intracellularly, thus compromising neuronal morphogenesis, hindering synaptogenesis and, consequently, limiting synaptic neurotransmission. Indeed, experimental data demonstrate that THC administration in vivo perturbs neuronal connectivity in mouse fetuses and infant offspring38,43 through CB1R engagement.34,44-46
The refinement of neuronal circuits continues during adolescent life with synaptic selection and pruning taking place to finalize synaptic connectivity in neuronal networks. Thus, cannabis use by teenagers can, at least partly, (re-)activate the mechanisms discussed for fetal development. Alternatively, THC can perturb cellular bioenergetics in neurons particularly by disrupting complex I of the mitochondrial respiratory chain,8 an adverse effect seen as long as 4-5 months after THC administration, at least in juvenile laboratory rodents.47 Thus, a second punchline for THC to impair brain development is through depleting cellular energy reserves to limit neuronal survival and function.
Endocannabinoid signaling in schizophrenia
High-potency cannabinoids increase the incidence of physiological (e.g., nausea) and psychiatric adverse outcomes (e.g., anxiety and psychosis). Notably, a correlation exists between first-time cannabis use during the individual’s life and the severity and relapse potential of cannabis action.48 Thus, it is becoming broadly accepted that children and adolescents are significantly more sensitive to cannabis, either directly or in transgenerational settings, and carry the risk of life-long impact on cognition, academic performance, impulsivity and social interactions.
One of the psychiatric disorders that has the clearest association with cannabis use is schizophrenia, a debilitating chronic disorder that exacts enormous personal, social and economic costs. Epidemiological studies have detected a 1.8-to-3.1-fold increase in the incidence of schizophrenia upon early cannabis use, identifying it as a major trigger for the disease to manifest.49 Conversely, cannabis is the drug of choice by schizophrenics despite its potential to exacerbate pre-existing psychotic symptoms or to trigger their re-emergence. Traditionally, schizophrenia is linked to alterations in the reward circuit including its midbrain (dopamine) and cortical components. In post-mortem studies, CB1R expression is increased in the prefrontal50 and cingulate cortices51 of patients with schizophrenia. Genetic evidence at the level of single nucleotide polymorphisms also associates CB1Rs (and even CB2Rs) with an increased likelihood of developing schizophrenia.52-54 CB1R polymorphisms were even used as predictors of changes in brain structure (e.g. white matter volume), thus qualifying as a gene-to-environment risk factor for the increased incidence of schizophrenia. It is noteworthy that these association studies are often population-specific with equally strong negative data reported elsewhere (see, e.g., Ref.55). Another correlate supporting a role for altered endocannabinoid signaling in schizophrenia is the increased bioavailability of AEA in the cerebrospinal fluid and blood of antipsychotic-naïve first-episode patients,56,57 which normalizes following antipsychotic treatment. The above data from human studies are also supported by animal models in which modifications to endocannabinoid signaling within the dopamine reward circuit (e.g., producing a striatal “hyperdopaminergic” phenotype at D1 and D2 dopamine receptor-expressing neurons that also harbor CB1Rs)58 behaviorally manifest as schizophrenia-like traits.
There is consensus that THC has no favourable effect for psychiatric disorders. Instead, CBD might be of medical use,59-66 given its non-psychotropic nature,67 with an emphasis on its non-CB1R-dependent neuroprotective properties instead68 (considering that CB1R modulation itself seems of limited benefit in schizophrenia)69. A major label to use CBD is because of its anxiolytic property (that is, treatment of a co-morbidity in schizophrenia) as shown in both animal models70 and humans.71-73 As such, CBD treatment improves serotonin neurotransmission,74 particularly at the level of serotonin 1A receptors,75,76 thus attenuating both stress responsiveness and impulsivity.74,77-79 Another indication for CBD use in schizophrenics and other heavy cannabis users is its ability to alleviate cannabis withdrawal symptoms,80-84 thus being medically preferred to treat addiction.
THC and CBD in neurological conditions
THC (and CBD) appears to have clinical benefit in neurological conditions associated with neuronal hyperexcitability and runaway network activity, such as epilepsy and pain. Mechanistically, THC can significantly suppress excitatory neurotransmission by engaging CB1Rs to prevent, e.g., seizure activity or pain-induced hypersensitivity (hyperalgesia). The market-leading example is Sativex® (a near-equivalent THC:CBD mixture) for the treatment of pain and spasms associated with multiple sclerosis. More recently, Epidiolex® (CBD only) received FDA approval for the treatment of severe epilepsy in children (e.g.,with Lennox-Gastaut and Dravet syndromes).85 The suggested mechanism of action for CBD rests largely on dampening neuronal excitability via engagement of TRPV1, GPR55 and likely the ENT-1 nucleoside transporter, resulting in significant seizure reduction.86
Summary
The medical use of Cannabis sativa stretches over millennia. However, it is fundamental research of the past ~50 years that has uncovered the molecular and cellular bases of phytocannabinoid action in the human body, and allowed us to rationalize adverse effects vs. medical benefits. Even though specific recommendations already exist for the medical use of THC and CBD, on-going (pre-)clinical research will continue to explore specific indications, as well as labels of use for these powerful natural compounds, supporting their relevance to modern medicine.
References:
1 Mechoulam R et al.: J Am Chem 1967; Soc 89: 4552-4 2 Mechoulam R, Gaoni Y: Tetrahedron Lett 1967; 12: 1109-11 3 Fattore L: Biol Psychiatry 2016; 79: 539-48 4 Murray RM et al.: World Psychiatry 2016; 15: 195-204 5 Turu G, Hunyady L: J Mol Endocrinol 2010; 44: 75-85 6 Castillo PE et al.: Neuron 2012; 76; 70-81 7 Keimpema E et al.: Trends Pharmacol Sci 2011; 32: 551-61 8 Jimenez-Blasco D et al.: Nature 2020; 583: 603-8 9 Herkenham M et al.: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990; 87: 1932-6 10 Katona I et al.: J Neurosci 1999; 19: 4544-58 11 Herkenham M et al.: J Neurosci 1991; 11: 563-83 12 O‘Keefe L et al.: Diabetes Obes Metab 2014; 16: 294-304 13 Chorvat RJ et al.: Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2012; 22; 6173-80 14 Pagotto U et al.: Endocr Rev 2006; 27: 73-100 15 Jenkin KA et al.: Cell Physiol Biochem 2010; 26: 879-86 16 Park B et al.: Placenta 2003; 24: 990-5 17 Straiker AJ et al.: Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1999; 40: 2442-8 18 Dennedy MC et al.: Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004; 190: 2-9 19 Van Sickle MD et al.: Science 2005; 310: 329-32 20 Sagredo O et al.: Mol Neurobiol 2007; 36: 82-91 21 Devane WA et al.: Science 1992; 258: 1946-9 22 Mechoulam R et al.: Biochem Pharmacol 1995; 50: 83-90 23 Sugiura T et al.: Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1995; 215: 89-97 24 Fezza F et al.: Molecules 2014; 19: 17078-106 25 Piomelli D: Nat Rev Neurosci 2003; 4: 873-84 26 Cadas H et al.: J Neurosci 1996; 16: 3934-42 27 Bisogno T et al.: J Cell Biol 2003; 163: 463-8 28 Cravatt B F et al.: Nature 1996; 384: 83-87 29 Maccarrone M: Front Mol Neurosci 2017; 10: 166 30 Dinh TP et al.: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 10819-24 31 Fiskerstrand T et al.: Am J Human Genet 2010; 87: 410-7 32 Marrs WR et al.: Nat Neurosci 2010; 13: 951-7 33 Kano M et al.: Physiol Rev 2009; 89: 309-80 34 Maccarrone M et al.: Nat Rev Neurosci 2014; 15: 786-801 35 Harkany T et al.: Trends Pharmacol Sci 2007; 28: 83-92 36 Harkany T et al.: Mol Cell Endocrinol 2008; 286: 84-90 37 Guzman M: Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 745-55 38 Mulder J et al.: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 8760-5 39 Berghuis P et al.: Science 2007; 316, 1212-6 40 Morozov YM, Freund TF: Neuroscience 2003; 120: 923-39 41 Grotenhermen F: Clin Pharmacokinet 2003; 42: 327-60 42 Metz TD & Stickrath EH: Am J Obstet Gynecol 2015; 213: 761-78 43 de Salas-Quiroga A et al.: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2015; 112: 13693-8 44 Tortoriello G et al.: EMBO J 2014; 33: 668-85 45 Harkany T et al.: Curr Opin Neurobiol 2008; 18: 338-45 46 Cristino L, Di Marzo V: EMBO J 2014; 33: 665-7 47 Beiersdorf J et al.: JCI insight 2020; 5: e135418 48 Di Forti M et al.: Lancet Psychiatry 2015; 2: 233-8 49 Andréasson S et al.: Lancet 1987; 2: 1483-6 50 Dean, B et al.: Neuroscience 2001; 103: 9-15 51 Zavitsanou K et al.: Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2004; 28: 355-60 52 Ujike H et al.: Mol Psychiatry 2002; 7: 515-8 53 Ishiguro H et al.: Biol Psychiatry 2010; 67: 974-82 54 Leroy S et al.: Am J Med Genet 2001; 105: 749-52 55 Tsai SJ et al.: Psychiatr Genet 2000; 10: 149-51 56 Giuffrida A et al.: Neuropsychopharmacology 2004; 29: 2108-14 57 Leweke FM et al.: Schizophr Res 2007; 94: 29-36 58 El Khoury MA et al.: Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2012; 38: 36-50 59 Winton-Brown TT et al.: Neuropsychopharmacology 2011; 36: 1340-8 60 Hallak JE et al.: Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2011; 35: 198-202 61 Englund A et al.: J Psychopharmacol 2013; 27: 19-27 62 Zuardi AW et al.: J Clin Psychiatry 1995; 56: 485-6 63 Zuardi AW et al.: J Psychopharmacol 2006; 20: 683-6 64 Leweke FM et al.: Transl Psychiatry 2012; 2: e94 65 Leweke FM: Schizophrenia Bull 2013; 39: 341 66 Ghabrash MF et al.: Psychiatry Res 2020; 286: 112890 67 Khoury JM et al.: World J Biol Psychiatry 2019; 20: 101-16 68 Campos AC et al.: Pharmacol Res 2016; 112: 119-27 69 Meltzer HY et al.: Am J Psychiatry 2004; 161: 975-84 70 Blessing EM et al.: Neurotherapeutics 2015; 12: 825-36 71 Zuardi AW et al.: Psychopharmacology 1982; 76: 245-50 72 Zuardi AW et al.: J Psychopharmacol 1993; 7: 82-8 73 Crippa JA et al.: Neuropsychopharmacology 2004; 29: 417-26 74 Campos AC et al.: J Psychiatric Res 2012; 46: 1501-10 75 Zanelati TV et al.: Br J Pharmacol 2010; 159: 122-8 76 Sartim AG et al.: Behav Brain Res 2016; 303: 218-27 77 Russo EB et al.: Neurochem Res 2005; 30: 1037-43 78 Gomes FV et al.: Psychopharmacology 2011; 213: 65-473 79 Breuer A et al.: PloS one 2016; 11: e0158779 80 Shannon S, Opila-Lehman J: Integr Med (Encinitas) 2015; 14: 31-5 81 Freeman TP et al.: Lancet Psychiatry 2020; 7: 865-74 82 Crippa JA et al.: J Clin Pharm Ther 2013; 38: 162-4 83 Trigo JM et al.: J Addict Med 2016; 10: 274-9 84 Allsop DJ et al.: JAMA Psychiatry 2014; 71: 281-91 85 Whiting PF et al.: JAMA 2015; 313: 2456-73 86 Gray RA, Whalley BJ: Epileptic disorders: international epilepsy journal with videotape 2020; 22: 10-15
Das könnte Sie auch interessieren:
Wie die Schwangerschaft Gehirn und Psyche beeinflusst
Eine Schwangerschaft verändert nicht nur den Körper, sondern auch das Gehirn und die Psyche einer Frau tiefgreifend. Diese Veränderungen markieren den Beginn einer eigenständigen ...
Ketamin-augmentierte Psychotherapie
Das schnell wirksame Antidepressivum (S-)Ketamin wird bei therapieresistenten Patient:innen effektiv eingesetzt. Als zentrale Komponente eines biphasischen Wirkmechanismus wird für ...
Der Stellenwert der antipsychotischen Depotbehandlung in der forensischen Psychiatrie
Schizophrenie und andere psychotische Störungen sind in der forensischen Psychiatrie aufgrund ihrer potenziellen Assoziation mit gewalttätigem Verhalten von hoher Relevanz. Ziel dieser ...